Page 7 - Seniorstoday Sep 2024 Issue
P. 7
preserving the teeth in a healthy condition to step out to seek oral health care. A
brings about a sense of well-being and variety of visual changes such as cataracts,
happiness. macular degeneration; audio changes such
as hearing loss can make communication,
General Health and Oral Health are patient education and oral healthcare
closely linked increasingly difficult.
Oral health can be compromised by a
number of systemic chronic and infectious Age Related Oral Changes
diseases that have oral symptoms. On
the other hand, oral diseases can lead to
infection, inflammation and other serious
impacts on overall health.
Connections between poor oral health
and major non-communicable diseases
like diabetes, cardiovascular diseases
and respiratory diseases are undisputed.
A simple example of diabetes, the
relationship between diabetes and gum
health is bidirectional. Hyperglycemia can
lead to gum disease, while gum disease like
periodontitis affect glycemic control.
People with poor gum health are more
prone to serious cardiovascular events
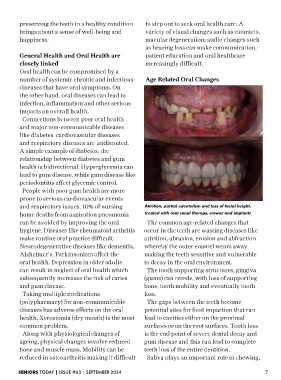
and respiratory issues. 10% of nursing Attrition, partial edentulism and loss of facial height,
home deaths from aspiration pneumonia treated with root canal therapy, crowns and implants
can be avoided by improving the oral The common age-related changes that
hygiene. Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis occur in the teeth are wasting diseases like
make routine oral practice difficult. attrition, abrasion, erosion and abfraction
Neurodegenerative diseases like dementia, whereby the outer enamel wears away
Alzheimer’s, Parkinsonism affect the making the teeth sensitive and vulnerable
oral health. Depression in older adults to decay in the oral environment.
can result in neglect of oral health which The tooth supporting structures, gingiva
subsequently increases the risk of caries (gums) can recede, with loss of supporting
and gum disease. bone, tooth mobility and eventually tooth
Taking multiple medications loss.
(polypharmacy) for non-communicable The gaps between the teeth become
diseases has adverse effects on the oral potential sites for food impaction that can
health, Xerostomia (dry mouth) is the most lead to cavities either on the proximal
common problem. surfaces or on the root surfaces. Tooth loss
Along with physiological changes of is the end point of severe dental decay and
ageing, physical changes involve reduced gum disease and this can lead to complete
bone and muscle mass. Mobility can be teeth loss of the entire dentition.
reduced in osteoarthritis making it difficult Saliva plays an important role in chewing,
SENIORS TODAY | ISSUE #63 | SEPTEMBER 2024 7