Page 8 - Seniorstoday Sep 2024 Issue
P. 8
lubrication of food, swallowing and speech. Common Dental Problems
Salivary glands can undergo degenerative 1 Dental caries (Cavities)
changes thus reducing the salivary 2 Periodontitis (Gum Disease)
output. Long-term medications such as 3 Wear in teeth – (Attrition, Abrasion,
antidepressants, anti-hypertensives, and Erosion, Abfraction)
antihistamines are commonly associated 4 Xerostomia (Dry Mouth)
with dry mouth, which in turn causes 5 Edentulism ( Tooth Loss)
difficulty in food swallowing (dysphagia), 6 Oral Cancer
cracked lips, fissured tongue, mucositis,
and cavities. 1 Dental Caries (tooth decay) is one of the
The oral mucosa is the lining of the oral most common bacterial diseases in man
cavity which becomes thinner and non- that causes the loss of tooth structure,
resilient with age. This can predispose potential pain, and untimely loss of teeth,
patients to cancer and pre-cancerous leading to impaired appearance and
lesions, which can be seriously life function.
threatening. In the ageing adult, the blunt chewing
Taste buds on the tongue decrease and surfaces of the teeth with flattened contacts
begin to shrink with age, altering the sense with adjacent teeth result in stagnation of
of taste and gets compounded in a dry food, making the surfaces prone to decay.
mouth. With gum recession, the root surfaces
are exposed to the oral cavity, making it
vulnerable to decay in absence of good oral
hygiene.
A reduced salivary output, lack of good
oral care, a diet high in carbohydrates and
sugar leads to rapid cavitation of the tooth
surface.
2 Periodontitis (gum disease) is seen in
over 60% of the older adults. There is a
loss of attachment of the gingiva (gum)
against the supporting tooth structure due
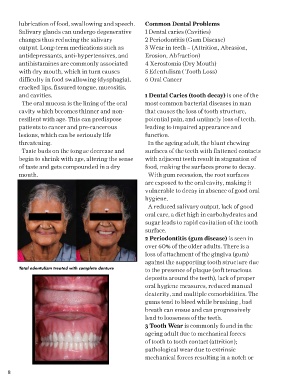
Total edentulism treated with complete denture to the presence of plaque (soft tenacious
deposits around the teeth), lack of proper
oral hygiene measures, reduced manual
dexterity, and multiple comorbidities. The
gums tend to bleed while brushing , bad
breath can ensue and can progressively
lead to looseness of the teeth.
3 Tooth Wear is commonly found in the
ageing adult due to mechanical forces
of tooth to tooth contact (attrition);
pathological wear due to extrinsic
mechanical forces resulting in a notch or
8