Ageing is a natural process, but how we age largely depends on how well we take care of our bodies. One of the key factors in maintaining good health as we grow older is ensuring that we consume enough antioxidants. These powerful compounds play a crucial role in protecting our cells from damage, reducing the risk of chronic diseases, and helping us feel more energetic and vibrant. But what exactly are antioxidants, and why are they so essential for senior citizens? Let’s explore.
Understanding Antioxidants
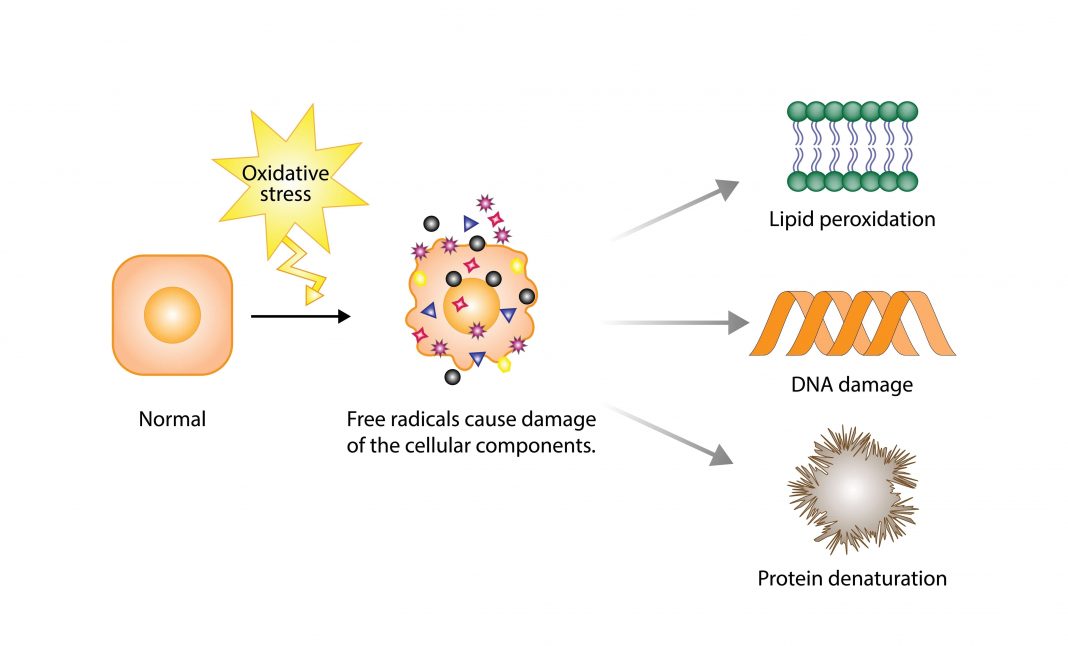
Antioxidants are molecules that help protect the body from oxidative stress caused by free radicals.
Free radicals are unstable molecules produced as a by-product of normal bodily functions, such as metabolism, as well as external factors like pollution, smoking, and unhealthy diets. When free radicals build up in the body, they can damage cells, leading to inflammation, ageing, and various diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and even cancer.
Antioxidants neutralise these free radicals, preventing them from causing harm. They act like the body’s defence system, helping to slow down the ageing process and support overall health.
Why Senior Citizens Need Antioxidants
As we age, our body’s natural ability to fight off free radicals weakens. This means that older adults are more susceptible to oxidative stress, which can accelerate ageing and increase the risk of various health problems. Here’s why antioxidants are particularly important for senior citizens:
- Protecting Brain Health
Cognitive decline is a common concern among older adults. Studies suggest that oxidative stress contributes to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Antioxidants like vitamin E, vitamin C, and flavonoids help protect brain cells from damage, supporting memory and cognitive function.
- Boosting Immunity
The immune system naturally weakens with age, making seniors more vulnerable to infections and illnesses. Antioxidants such as selenium, vitamin C, and zinc play a crucial role in strengthening immunity, helping the body fight off colds, flu, and other infections more effectively.
- Supporting Heart Health
Heart disease is a leading cause of illness among older adults. Antioxidants such as flavonoids (found in dark chocolate and berries) and lycopene (found in tomatoes) help lower bad cholesterol, reduce inflammation, and improve blood circulation, thus supporting cardiovascular health.
- Maintaining Healthy Skin
Ageing skin becomes more prone to wrinkles, dryness, and damage from UV rays. Antioxidants like vitamin E and beta-carotene help protect the skin from oxidative stress, keeping it healthier and more resilient.
- Reducing Inflammation and Joint Pain
Many seniors suffer from conditions like arthritis, which causes joint pain and stiffness. Antioxidants such as curcumin (found in turmeric) and polyphenols (found in green tea) have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce pain and improve mobility.
- Preventing Age-Related Eye Diseases
Conditions like cataracts and macular degeneration are common among older adults. Antioxidants such as lutein and zeaxanthin, found in leafy greens and eggs, help protect the eyes from oxidative damage and support long-term vision health.
Best Sources of Antioxidants for Seniors
While our bodies produce some antioxidants naturally, the majority must come from a well-balanced diet. Here are some of the best antioxidant-rich foods to include in a senior’s diet:
- Fruits: Berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries), oranges, grapes, and apples
- Vegetables: Spinach, kale, carrots, tomatoes, and bell peppers
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and sunflower seeds
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, oats, and quinoa
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and black beans
- Herbs and Spices: Turmeric, cinnamon, ginger, and garlic
- Dark Chocolate: A small amount of high-quality dark chocolate (70% cocoa or more) is rich in flavonoids and beneficial for heart health
Should You Take Antioxidant Supplements?
While it’s always best to get nutrients from whole foods, some seniors may struggle to consume enough antioxidants due to dietary restrictions, digestion issues, or chronic conditions. In such cases, antioxidant supplements may be helpful. However, it’s important to consult a doctor before taking any supplements, as excessive intake of certain antioxidants can be harmful.
Lifestyle Tips to Maximise Antioxidant Benefits
In addition to eating an antioxidant-rich diet, adopting a healthy lifestyle can further support overall well-being:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water helps flush out toxins and supports cell function.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity boosts circulation and reduces oxidative stress.
- Get Enough Sleep: Restorative sleep helps the body repair itself and fight off free radical damage.
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: These habits increase oxidative stress and accelerate ageing.
- Manage Stress: Practising mindfulness, meditation, or engaging in relaxing activities helps lower inflammation and improve overall health.
Antioxidants are essential for maintaining health and vitality as we age. By incorporating antioxidant-rich foods into your daily diet and leading a balanced lifestyle, you can protect your body from oxidative stress, reduce the risk of age-related diseases, and enjoy a longer, healthier life. Remember, small changes can make a big difference—so start adding more colourful fruits and vegetables to your plate, and let your body reap the benefits!