What is sleep?
Sleep is a state where, for a brief period, our awareness to the external stimuli reduces, our body processes slow down.
What happens during sleep?
Till recently, it was believed that sleep was just a dormant period, when the body and the brain rested. We now know differently. The brain and the body are, in fact, very busy, repairing tissues and rejuvenating.
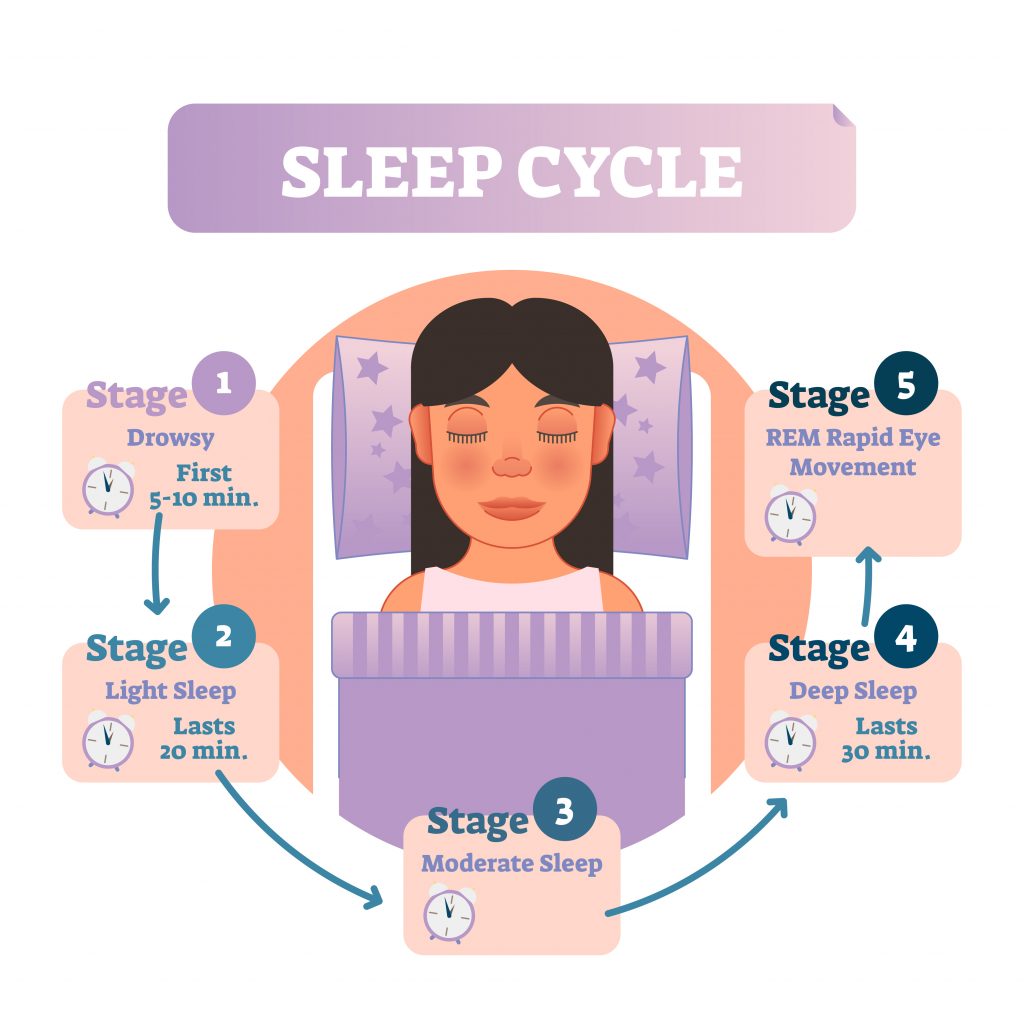
Throughout the time we sleep, our brain goes through cycles of two types of sleep- REM and NON REM
Non Rem– this is the first type, and in itself consists of four parts- the first part hovers between sleep and wakefulness; if woken up in this phase, you might not even realize you slept. The second part is light sleep, with the heart beat the breathing regularizing and slowing down. The third and fourth part is deep sleep, and it’s difficult to wake up; if you do so, you may feel groggy and dis oriented.
The body and brain use this time to repair muscles, build immunity regenerate tissues.
Rem ( rapid eye movement) – In this second type, the heart rate and breathing become rapid again, it’s not as deep as Non Rem, and is usually the part where you get dreams. The 1st cycle of REM starts about one and a half hour after you sleep, and lasts for about 10 minutes. The timing increases in consecutive cycles.
This sleep is very important, as it stimulates the parts of the brain that help in learning. It also promotes protein production.
Circadian rhythm
This rhythm controls your sleep – wake cycle over a period of 24 hours. Influenced by light and dark, as well as external environmental factors, the brain receives and sends out signals that monitor our sleeping patterns.
How much sleep is healthy?
Though essential at any age, the number of hours required varies with age. Infants require maximum sleep, around 14 to 17 hours a day, as their body is developing…from here on, it decreases. Children and teens require between 11 to 13 hours of sleep, while adults need 7 to 9 hours. It decreases further as you touch the geriatric age group.
Best position
We spend between 6 to 8 hours every day sleeping, and it’s important to be comfortable. Every individual has a different position that’s preferable…on the sides, back etc. There are, obviously, advantages and disadvantages to all the positions –
The Back –
PROS – Sleeping on the back is probably the best; it aligns your vertebrae, gives adequate support to the spine. Sleeping on your back in a propped up position helps relieve nose block and acidity. It also provides maximum support to the neck, preventing neck pain.
CONS – It’s not a favorable position if you have sleep apnea, as it can cause airway collapse. Also not recommended during pregnancy. In some cases, it can lead to lower backache, but this can be corrected by sleeping with a pillow underneath the concerned area.
The Sides – 60% of people find this position more comfortable, especially males.
PROS – It’s quite beneficial, as it also provides adequate alignment to the spine, especially with support. It could also reduce acidity and snoring, so people with reflux esophagitis and sleep apnea benefit from this position. Pregnant women, too, would find this position comfortable.
CONS – This position can lead to stiffness and pain in the shoulders, so if you suffer from shoulder pains, avoid or keep changing your sleeping position. Having your face pressed to the pillo3ws for an extended time could also give rise to wrinkles.
The preferable side – Of the two sides, sleeping on the left side is preferable, as it may reduce heartburn as well as regularize the bowel movement.
Fetal position – This is a variation of the side position, but with the knees pulled up towards the chest.
PROS – Pregnant women, especially, find this position comfortable as it prevents the pressure of the enlarged belly to reach the heart, ensuring adequate blood circulation.
CONS – it could leave you feeling sore. Also, if you fold your knees too tightly, it could lead to breathing difficulties.
The Stomach – This position is the least preferred, though a few people may find it comfortable
PROS – It does reduce snoring and sleep apnea.
CONS – it is responsible for a lot of neck and back stiffness as well as pain, as you cannot support the spine with pillows and cushioning. It can also cause muscle strain. If you do find this position to your liking, use a very thin pillow, or avoid one completely. Also choose a firm mattress that doesn’t let your body sink into it.
At the end of the day, the best position for you is one which lets you get a restful and uninterrupted sleep for a few hours, with a feeling of freshness in the morning. If you’re current position allows you to do so, you do not need to change. If you feel there’s room for improvement, try new ones.

Foods that help
Fish
Fish, especially the fatty kind, is very rich in Vit d and omega 3 fatty acids, both of which regulate serotonin production. This in turn helps manage the sleep cycles.
Research Has found that people eating fatty fish on a regular basis, tend to have better sleep patterns than those having other meats, This has been attributed to the Vit d and omega 3 levels in the fish.
Turkey
Turkey has high levels of tryptophan, an amino acid which helps in the production of the hormone melatonin. It’s also a very rich source of protein, which is supposed to induce better sleep.
Eggs
Eggs by themselves are very rich in tryptophan, and can be a useful tool in inducing sleep.
Lettuce
Not only does lettuce have sleep inducing properties, it is believed to have a sedative like effect, probably due to the lactucorium present in it.
Barley
Barley is a powerhouse of sleep promoting compounds, like GABSA, tryptophan, magnesium and calcium. You can add barley grass powder to your smoothies and salads.
Figs
A rich source of calcium, magnesium and iron, figs help in improving blood flow to the body, and in distribution of vital hormones too.
Sweet potato
Not only are they generally healthy, they are great sources of calcium, magnesium and potassium. They can help in lowering the blood pressure and relax, making them a good option to have before bedtime.
White rice
White rice has a high glycemic index, due to its high carb and low fiber content. Studies have shown that foods with a high GI help inducing sleep.
Honey
The glucose present in honey reduces orexin levels, a hormone that causes alertness. The sugars present in honey also help in carrying and distributing Tryptophan to the brain.
Tofu
Its high protein content, along with the calcium and isoflavone, help in the production of serotonin, which helps you sleep better.
Oatmeal
Similar to white rice, its high carb and fiber content give it a high GI, which makes it a sleep inducing food. Having oatmeal about an hour before bedtime can help a person sleep well.
Kale
Besides being a powerhouse of vitamins, kale has very high calcium content. The calcium helps melatonin production by triggering the brain to release tryptophan.
Popcorn
A whole grain, popcorn is a house of fiber and carbs. Carbs help release of tryptophan, which helps induce sleep.
Hummus
Made of chickpeas, hummus is rich in folate, calcium. Multi vitamins and protein, all of which help sleep, by producing melatonin and serotonin. Hummus is naturally rich in melatonin too, making it an ideal midnight snack!
Dark chocolate
The magnesium present in dark chocolate helps regulate the circadian rhythms, in turn controlling your sleep cycles.
Almonds
Almonds are very rich in melatonin, a hormone that regulates our circadian rhythm. One ounce of almonds contains about 75 gms of magnesium and calcium, which also help sleep. Magnesium helps induce sleep by reducing inflammation. It may also reduce the levels of cortisol, the stress hormone. Try including them as a small snack mid meals, on a daily basis.
Walnuts
With a high content of melatonin, walnuts are a good addition to your diet. They are also good sources of magnesium, folate and calcium, all of which can help the sleep pattern.
Nut butter
Almond or peanut butter is a very good source of protein, Vit B6, B12 and carbs, which boost production of melatonin. Nut butter with toast or crackers makes for a great snack option.
Kiwi
A small study showed that people consistently having kiwifruit about an hour before bedtime, showed improved sleep patterns. This is possibly because kiwi is rich in melatonin, magnesium, calcium, flavonoids and folates, all of which aid good sleep. Kiwi is known to be rich in Serotonin, which promotes good sleep. It could also be due to the Vitamin C and carotenoids, anti-oxidants which help sleep.
Banana
Banana peels are very rich in tryptophan, while bananas are rich in magnesium, both of which are known to induce a healthy, good sleep. They are also rich in potassium, which is essential to a deep sleep.
Grapes
Grapes have naturally occurring melatonin, the hormone that is instrumental in setting the sleep cycle. Make sure you have some twice or thrice a week.
Yogurt
Yogurt, besides being a source of protein, also has high calcium content. Calcium is necessary to process melatonin, which in turn helps regulate the sleep cycle.
You can add nuts and fruits to it for added benefits.

Drinks that soothe
Chamomile tea
One of the traditional remedies for insomnia, chamomile is believed to be rich in a flavonoid called apigenin, which helps us sleep better. It is said to reduce depression too. A cup of hot chamomile tea before bedtime can be a very relaxing nighttime ritual.
Warm milk
Not only is milk rich in melatonin, it also has high levels of calcium and tryptophan, all of which promote good sleep.
Of course, it’s possible that the age old belief of warm milk leading to peaceful and restful sleep is what works. In any case, a glass of warm milk at bedtime can be quite effective.
Cherry juice
Besides being a rich source of melatonin, serotonin and potassium, cherries also have a high content of anti-oxidants polyphenols. Studies have found a positive relationship between polyphenols and sleep.
It’s also said to reduce swelling and pain post exercise.
Passion flower tea
Passion flower tea is another one of the traditional sleep remedies. Its high content of apigenin helps relax and soothe the brain by producing GABA, which inhibits glutamate, a stress inducing chemical.
Insomnia
A common disorder, insomnia could mean difficulty sleeping, waking up frequently at night or feeling unrested on waking up
It generally affects women more than men. It’s also common in elders.
Insomnia could be short-term- lasting from a few days to a few weeks. The causes are usually stress or hormone related.
Some people, however, suffer from chronic insomnia, a condition that can persist for months and years, eventually affecting their health.
What causes it?
To pinpoint a specific cause is difficult. However, a number of things can contribute to insomnia.
Stress or anxiety
Sleeplessness due to stress is common, and can keep you up at night. Trauma, a tragic event, financial difficulties can all become the cause for insomnia. The condition gets aggravated by people stressing about the sleeplessness itself, often associating bedtime with wakefulness.
Anxiety and difficulties at work, health problems are also likely triggers for insomnia.
Inconsistent routine
Having an inconsistent bed time, taking long naps during the day or, sometimes, even getting too tired can all led to insomnia.
The bedroom environment
Loud noise, bright lights, a very warm or cold room can cause insomnia.
Lifestyle
Shift changes at work, frequent long flights or those across time zones can cause insomnia. Indulging in caffeine, alcohol or recreational drugs just before bedtime will also affect your sleep pattern.
Medication
Certain medicines like steroids, anti-depressants, NSAIDS, beta blockers can either cause or aggravate insomnia.
Health conditions –
Physical – Diseases like arthritis, chronic obstructive lung disease, and angina can keep you awake at night due to pain or breathlessness. Certain neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s can also cause insomnia. Hypothyroidism, sleep disorders like sleep apnea or narcolepsy all contribute to this condition.
Mental –
Mood disorders like depression, anxiety disorders, posttraumatic stress disorder, and schizophrenia are known triggers of insomnia.
In fact, insomnia is one of the symptoms of depression- about 80% of people with depression will present with it.
How does it affect you?
Less sleep can affect multiple facets of your life. Your cognitive functions become slower, the mind is foggy. Making decisions can become difficult. It might also aggravate any mental disorders you might have a pre disposition to, like depression and anxiety. Often, it becomes a vicious cycle.
Foods that increase insomnia
Caffeine
The most common stimulant consumed, it’s usually had as coffee or tea, but it is found in chocolates too. People usually have it to stay awake and alert, but having too much of caffeine can really upset your sleep cycles.
Black tea
Black tea has about 2/3rd the amount of caffeine as coffee, and can keep you up well into the night.
Alcohol
A lot of people consume alcohol to relax themselves and invite sleep. However, alcohol can actually do the reverse- it disrupts the sleep cycle and pattern, eventually causing insomnia. It can also mess with your body’s circadian rhythm.
Energy drinks
Energy drinks are often a combination of caffeine and sugar, both of which are not conducive to good sleep.
Sugary food
Food high in sugar leads to increased glucose in the body, with increase in insulin to counter the effects. This leads to disturbed sleep, with increase in short periods of sleep.
Celery
Celery, or for that matter, any water rich food, can act as a diuretic, which means you might need to get up frequently to relieve yourself, disturbing your sleep in the process.
Fried food
Fried food is quite heavy, and can cause reflux and a bloated tummy, especially if had at night. It also takes longer to digest and can cause trouble while sleeping.
Cakes and pastries
Foods like cake, rich in sugar as well as fat, can cause heaviness and reflux, especially when one tries to sleep. The high glucose levels can also lead to increased insulin levels and sleep disturbances.
Tomatoes
Tomatoes, though very healthy are rich in an amino acid called tyramine, which triggers the brain to release hormones that stimulate the brain activity, making it difficult to relax and sleep soundly.
Spicy food
Spicy food can irritate the stomach lining, causing reflux and nausea, especially when you’re lying down.
Salty food
Salty food causes an increase in blood pressure, which in turn leads to other complications, including sleep disorders.
Aged/ cured foods
Aged foods are usually high in sodium, and can cause fluid retention and hypertension. They also have certain amino acids that stimulate the brain, possibly making it difficult to sleep.

Sleep Hygiene
The habits that we cultivate and the routine we follow to get a good night’s sleep is called sleep hygiene. Some of the habits that work well are:
Sleep schedule
Try to maintain a schedule of your sleeping and wake up timings, and follow it on a daily basis.
Don’t sleep in
It’s very tempting to keep late hours over weekends, stay up late, and wake up at leisure. Try not to make a habit of it. The more you are consistent with your schedule, the better it will be for you.
Short naps
Short naps in the afternoons are quite common, and to an extent, healthy. But as far as possible, try to keep them short- 30 to 45 minutes. A long nap in the afternoons often leads to sleepless nights.
Mind what you eat
Avoid eating foods which cause insomnia or discomfort at night. Preferably, keep a gap of about 2 hours between your dinner and bedtime. Avoid alcoholic or caffeine based drinks before going to bed.
Physical activity
Physical activity and exercise should be done in the daytime. About 30 to 45 minutes of walk or swimming a day is ideal, but try to keep a gap of about 3 hours between the exercise and your bedtime.
Control exposure to light
Avoid using gadgets which are backlit, like an e book or a laptop, right before bedtime.
Make the environment comfortable
Make sure that your bedroom is comfortable and conducive to sleep. The temperature shouldn’t be too hot or cold, the lights should be dim. Avoid white noise in the bedroom.
Breathe deep
Practicing certain breathing exercises before bedtime can help relax the body and make you sleepy.
Don’t force yourself
Sleep only when your body signals that it’s tired. Forcing yourself to sleep doesn’t help. It could just lead to anxiety about the sleeplessness, and leave you feeling exhausted.
There are times when, once you get up, sleep evades, no matter what. Just get up and engage in some activity that relaxes you. Read a book, listen to soothing music, have glass of warm milk.
Avoid dependence on medication
Try to avoid too much medication, it might make you dependent on them and it could be harmful.
Medical intervention
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
This therapy helps you to identify and rectify the problems, thoughts and behaviour which could cause insomnia. It also trains you to cultivate habits that could counter these issues.
Medication
At times, taking sleeping pills for a short period of time, under supervision, could be the best treatment.
Sleep is something we all compromise on- for work, family, parties and get togethers. While doing so occasionally is acceptable, making a habit of it is only going to harm you in the long run. So remember to catch your forty winks!









